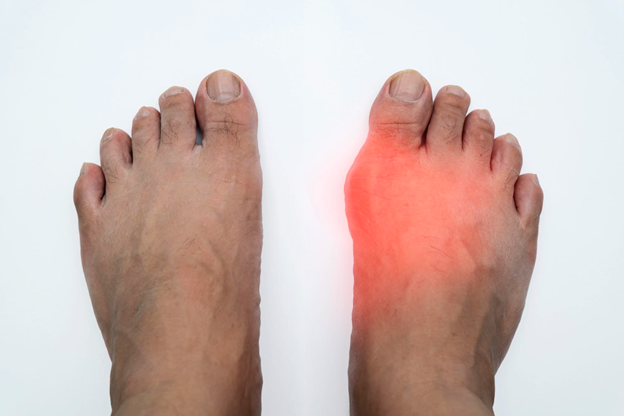
Gout is a type of arthritis that causes sudden, intense pain and swelling in the joints, most commonly in the big toe. It occurs when there’s too much uric acid in the blood, and this acid forms sharp crystals in the joints.
What is Gout?
Gout happens when uric acid builds up in the body and forms crystals in your joints, leading to pain and inflammation. Uric acid is produced when your body breaks down purines, substances found in certain foods. Normally, uric acid is eliminated through urine, but if the body produces too much or doesn’t get rid of enough, it can lead to gout.
Gout attacks can happen suddenly and are often very painful, lasting from a few hours to several days. It most commonly affects the big toe, but other joints like the knees, ankles, and wrists can also be affected.
What Causes Gout?
Several factors can cause gout, including:
- High Uric Acid Levels: The main cause of gout is an excess of uric acid in the blood.
- Diet: Eating foods rich in purines, such as red meat, shellfish, and alcohol, especially beer, can raise uric acid levels and trigger gout attacks.
- Obesity: Being overweight can increase the production of uric acid and make it harder for the body to remove it.
- Genetics: If gout runs in your family, you may be at higher risk.
- Health Conditions: Diseases like high blood pressure, diabetes, and kidney problems can raise uric acid levels.
- Medications: Some medicines, such as diuretics for high blood pressure, can increase uric acid levels and trigger gout.
Symptoms of Gout
The main symptoms of gout are:
- Severe Joint Pain: This often starts suddenly, especially in the big toe, but can affect other joints as well.
- Swelling and Redness: The affected joint may become swollen, red, and warm to the touch.
- Tenderness: The joint can be so sensitive that even the lightest touch may cause severe pain.
- Limited Mobility: Swelling and pain can make it difficult to move the joint properly.
Gout attacks typically come on quickly and can last from hours to days. However, if left untreated, they can become more frequent and cause long-term joint damage.
Treatment for Gout
While gout cannot be fully cured, it can be managed. Treatment typically focuses on relieving pain and lowering uric acid levels to prevent future attacks.
- Medications: can reduce pain and swelling during an attack.
- Lifestyle Changes:
- Dietary Adjustments: Avoid foods high in purines, such as red meat, shellfish, and alcohol. Drinking plenty of water helps your body flush out uric acid.
- Weight Management: Losing weight can help lower uric acid levels and reduce the frequency of attacks.
- Limit Alcohol: Especially beer, which can raise uric acid levels.
- Preventive Care: Regular monitoring of uric acid levels, along with long-term medications, can help manage gout and prevent flare-ups.
Gout is a painful but manageable condition. With the right treatment and lifestyle changes, you can control symptoms and prevent future flare-ups. At Unity Gastro & Liver Hospital, we provide expert care and support to help you live a pain-free life.
Don’t wait—contact us today to schedule a consultation and take the first step toward better joint health!