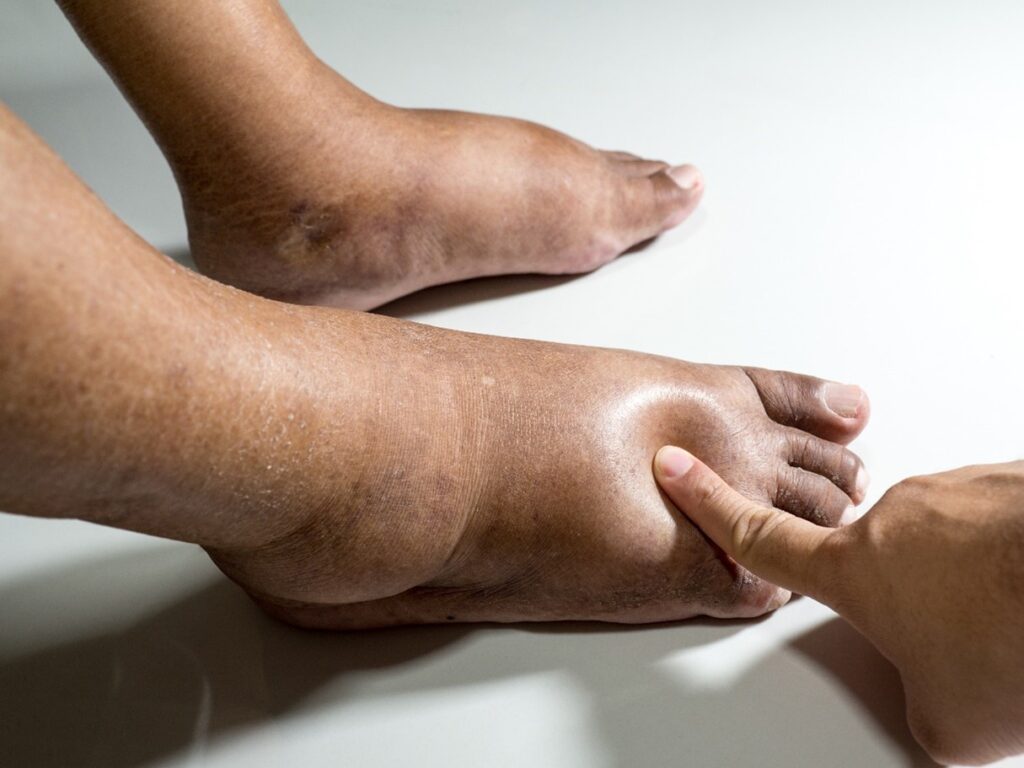
Diabetes significantly increases the risk of developing severe foot conditions, often due to
- Neuropathy (nerve damage)
- Poor circulation
These complications can escalate into serious problems, such as infections that might necessitate amputation if not managed quickly.
Understanding and addressing these risks is vital to preserving foot health.
Common Foot Issues in Diabetes
Individuals with diabetes might face several foot-related problems:
- Ulcers and Blisters: These often occur in areas where the shoe rubs against the foot and, without timely treatment, can lead to severe infections.
- Corns and Calluses: These are caused by skin thickening in response to pressure and can lead to further complications if not properly managed.
- Fungal Infections: Conditions like athlete’s foot are more prevalent and can be more severe due to weakened immune systems.
- Ingrown Toenails: These can become infected and are more problematic in diabetic individuals.
Symptoms to Monitor
Identifying foot issues early can help avoid further complications. Symptoms include:
- Persistent pain or swelling
- Any skin or nail changes, including cuts, blisters, or discoloration
- Indicators of infection, such as pus or a bad smell.
- Severe Complications
Neglected foot care can lead to dire consequences:
- Gangrene: Marked by tissue death from inadequate blood flow, this condition demands urgent medical care.
- Charcot Foot: This severe form of arthritis can deform and disable the foot, emphasizing the need for early intervention.
Causes of Foot Conditions
Foot complications in diabetes are primarily caused by:
- Diabetes-Related Neuropathy: This condition reduces the ability to feel pain, heat, or cold, which can lead to unnoticed injury or infection.
- Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD): PAD makes it difficult for infections to heal due to poor blood circulation.
Diagnosis and Treatment
Foot conditions are diagnosed through physical exams and, if necessary, imaging tests like X-rays.
Treatment typically involves:
- Wound Management: Cleaning wounds and applying appropriate dressings.
- Offloading: Using devices to reduce pressure on sensitive areas.
- Medication: Antibiotics to treat infections, and in severe cases, surgery might be required.
Preventive Care
Prevention is paramount and involves several steps:
- Daily Inspections: Use a mirror if needed to check feet daily for injuries.
- Proper Footwear: Choose footwear that provides a good fit and safeguards your feet.
- Skin Care: Keep feet clean and moisturized to prevent cracks and dryness.
- Avoid Smoking: Smoking impairs circulation, exacerbating foot problems.
Regular Medical Check-ups
Regular visits to a doctor for foot examinations ensure that any problems are detected and treated early.
By controlling blood sugar levels and maintaining rigorous foot care, individuals with diabetes can greatly lower their risk of serious foot conditions.
Prioritize your foot health by consulting your doctor about the best care practices for your feet today!